Stroke
Crossroad
Research theme: Rehabilitation and prevention
Clinical pillar: Stroke and other forms of acquired brain injury
Rehabilitation aims to stimulate recovery and to prevent problems in daily life functioning. This is established by reducing, compensating for, or teaching people to live with problems in daily life functioning and to optimise societal participation and increase the quality of life of patients and their informal caregivers from a bio-psycho-social perspective (ICF model WHO, see figure). In this research line we focus on patients with stroke and other forms of acquired brain injuries such as traumatic brain injury and brain damage due to a cardiac arrest.
Research focus:
- Development of new instruments for diagnostic, prognostic and evaluative purposes.
- Investigation of changes in functioning over time.
- Identification of prognostic factors and
- Development and evaluation of the clinical and cost-effectiveness of interventions.
Unique contributions and highlights
The research projects are embedded in the Limburg Brain injury Center (www.hersenletsellimburg.nl) and Adelante brain injury research in close collaboration with other regional health care organisations and patient organisations.
Currently we are developing and evaluating new interventions from two perspectives. On the hand, we aim to stimulate neuronal recovery by combing behavioral treatments (rehabilitation) with non-invasive brain stimulation for stroke patients with neglect. On the other hand, we adapt existing evidence-based psychological treatments to fit patients with cognitive deficits.
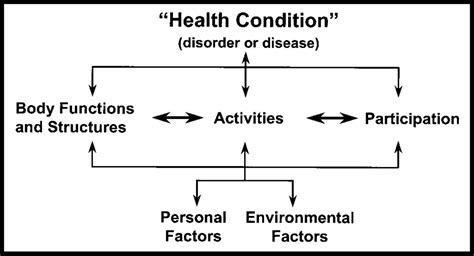
International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) model of the World Health Organisation (WHO 2001, 18).
