Epilepsy
Crossroad
Research theme: Neuroimaging
Clinical pillar: Epilepsy
We apply various advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques and data analysis methods to patients with epilepsy, in order to answer fundamental and clinically relevant neurological questions, and thus obtain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of epilepsy and its comorbidities. Activities are in collaboration with the Academic Centre for Epilepsy and the Centre for epilepsy Kempenhaeghe.
Unique contributions and highlights
Current Projects
- Development of novel MRI acquisition and image analysis techniques, with a focus on network methods, in patients with various forms of epilepsy.
- Structural and functional imaging network markers of the neuronal substrate of cognitive co-morbidities in adult and paediatric patients with epilepsy.
Cerebral networks and cognition
Using diffusion- and functional-MRI, combined with graph analysis. We showed in paediatric and chronic epilepsy, that cognitive dysfunction is associated with altered functional and structural networks.
(Vlooswijk et al., Neurology. 2011;77(10):938-44 & Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(10):1018-27; and Vaessen et al., Cereb Cortex. 2013;23(8):1997-2006)
Imaging of myelin
An abnormal neurodevelopmental myelination has been implicated in children with epilepsy. We developed MRI myelin imaging techniques, and showed that frontal myelin-water content is significantly lower in children with epilepsy. (Drenthen et al. Neuroimage. 2019;195:333-339 & Epilepsia. 2019;60(8):1689-1696)
Ultra-High field MRI
Ultra-high field MRI (≥7T) holds promise for epilepsy, as it allows for better visualization of brain structure, function, and metabolism (e.g. van Veenendaal et al. Neuroimage Clin. 2018;19:47-55). The National Epilepsy Foundation funded in 2019 a project in which the merits of ultra-high field MRI will be investigated in chronic, drug-resistant focal epilepsy.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) protects the central nervous system against toxins in the bloodstream and maintains the homeostasis. BBB dysfunction has been associated with epileptogenesis, though the exact course is unclear. In a translational neuroimaging study, funded in 2019 by ZonMW and the National Epilepsy Foundation, we will investigate Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a predictor for post-stroke epilepsy.
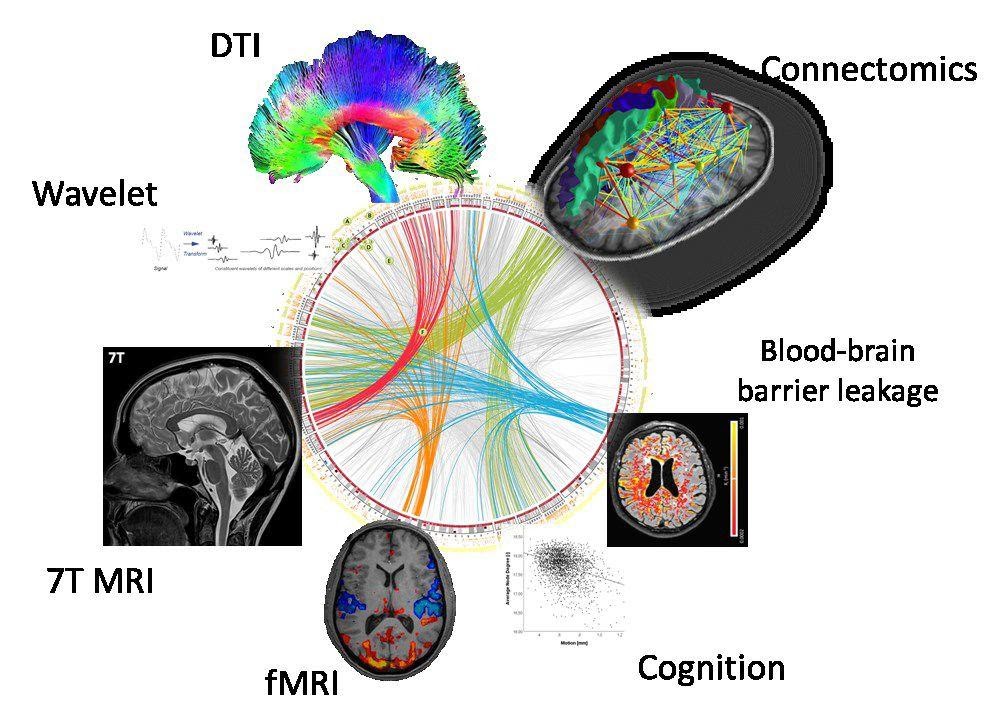
Overview of Neuroimaging & Epilepsy research.
