icis-e-book-12.pdf
(209.59 KB, PDF)
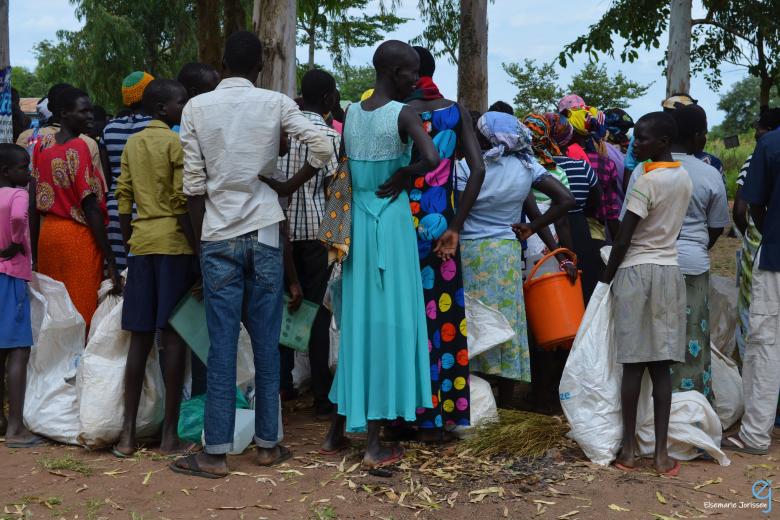
… an integral part of the current phase of capitalist development. Illegal practices are present in routine production in factories and workshops, in the widespread theft of intellectual property, in the growth of counterfeit products, in a variety of exchange and trading activities and, crucially, in flows of money and money laundering activities in centres of global finance that convert money generated in illegal activities into legitimate money capital in the formal mainstream economy (Hudson, … permanently resident or established in any specific national jurisdiction. But these have grown to become the sites of a majority of many of the financial transactions of the global economy: over 50% of international bank lending, approximately 33% of foreign direct investment, and 50% of global trade is routed on paper via OTHs which account for only 3% of world GDP (Christensen, 2011). Part III The socio-economic dimension 138 From one point of view the competitive success of particular companies … 140 Briefly, such options include the informal and social (or alternative) economy and the emerging “zero marginal cost” economy.11 This chapter focuses on the first of these. The informal and social (or alternative) economy is a system of trade or exchange used outside state-controlled or money-based transactions. It includes barter and exchange of goods and services, mutual self-help, self-employment and subsistence activities. The informal economy has grown continuously in most developing …