Microphones, farmers and forest ecologists; System Earth Science is taking shape
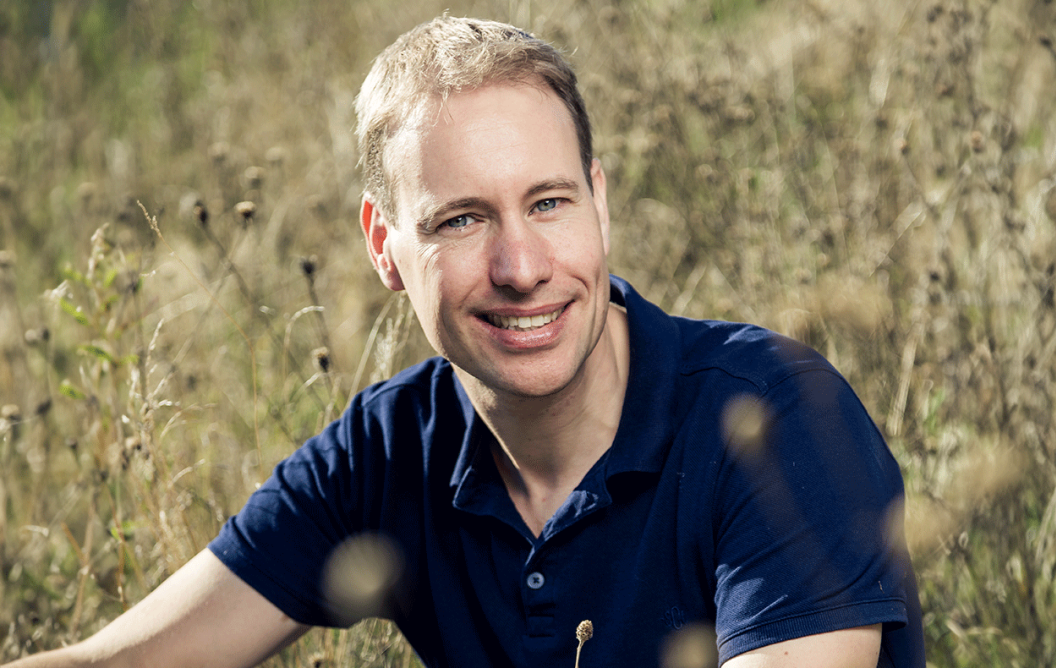
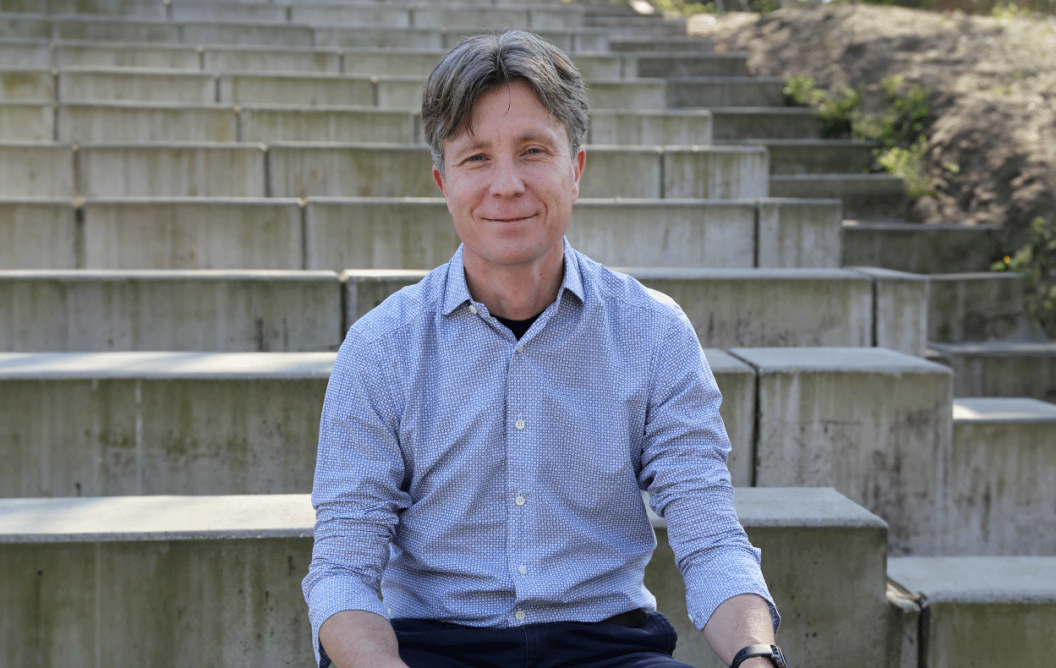
Everything on Earth is interconnected and has an impact on everything else. Nothing is isolated. This insight prompted the emergence of the very transdisciplinary field of Earth System Science. The field is gaining a foothold at the Brightland Campus Greenport Venlo in the form of the research institute System Earth Science. The institute's founders, Roy Erkens of the Maastricht Science Programme and Pim Martens of University College Venlo, discuss it.
As you stroll through the woods, you can hear birds chirping and the wind rustling through the trees. In addition, there might be creaking, a dog barking, or the sound of a rumbling tractor and fast-moving traffic on the highway in the distance. It is impossible for someone who studies the sounds of the forest to be content with only listening to the birds or the people who drive, walk, or farm there. It will require you to study the whole thing. Such a systems view of the forest, its environs, and, as the name implies, the entire Earth can be found at the Faculty of Science and Engineering's new research institute System Earth Science.
Context
"Everything has context," states Erkens, regarding the relatively new science and engineering discipline of Earth System Science. “For instance, when researching novel crops for agriculture, we consider not only the plants themselves but also their environment, including all the biological, geological, and social elements as well as the way these elements interact with one another.” Martens adds: "We study how people influence system Earth and are influenced by the components of that system."
Transdisciplinary
According to Erkens, "System Earth Science (SES) is not a shell around separate groups; rather, in SES, researchers work together in one group. Our goal is to do research that is truly transdisciplinary, involving both scientists and members of the community, like citizens and entrepreneurs.” According to Martens, transdisciplinary research calls for a distinct kind of researcher. “We deliberately seek out people who are able to move between disciplines, not just within SES, since the world extends beyond Venlo and Maastricht.” A forest ecologist will shortly begin working as a professor of ecology and biodiversity at SES. Beginning with just the two of them last year, Martens and Erkens intend to include fifteen researchers in SES next year.
Future
Let's return to our stroll in the forest and its implications for SES's future. Microphones pick up on all the sounds and whistling as you walk. A study being prepared by SES and Department of Advanced Computing Sciences intends to use these sound recordings to map biodiversity in food forests.
What are the researchers hoping to accomplish? Martens responds, "We hope to positively impact System Earth through our research. Based on their technical, biological, earth scientific, and/or social knowledge, we teach our students to work on these changes in an interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary manner. Not only do we want to encourage society to start using the findings of our research, but we also want people to ask us questions. Now that the seed has been sown, it will grow.”
Research themes
In order to develop solutions for a more resilient future planet, the five SES research themes concentrate on the functioning of the Earth system in the past and present, the role of humans in this system, and urgent environmental concerns including climate change and biodiversity loss. The five themes are listed below.
Evolutionary Diversity
What do the past and current state of plant evolution tell us about the likelihood of plants surviving in a world affected by humans in the future? Consider the dandelion that becomes accustomed to living in a city.
Ecology and Biodiversity
This theme studies at the interaction between, for example, plants and insects or plants and microorganisms. It also looks into the conservation of biodiversity in the context of climate change. Think about the use of drones to monitor the health of crops.
Planetary Health
How is the health of people, animals, and plants in the rural areas of the Netherlands affected by climate change? What impact does this have on the land's crops, our food supply, and the farmers' own lives?
Sustainable Food Systems
How can new agricultural methods increase food production, conserve biodiversity, and have minimal adverse effects on the environment all at once?
AI for biodiversity
How can artificial intelligence be used to support biodiversity at all levels? This involves, for instance, determining patterns in genetic variety, finding new species based on collected plant material, or quantifying biodiversity in forests to track changes.
Also read
-
Working at UM: “a life-changing experience”
"I am proud that our new Circular Plastics group published its first completely in-house research," Kim Ragaert says. She founded the research group three years ago, when she moved to Maastricht. Her work has laid the foundations for many innovations in the field of plastic recycling, and she is...

-
How does the universe taste?
Gerco Onderwater investigates the flavour of the universe while guarding the flavour of the Maastricht Science Programme. On 31 May, during his inaugural lecture, he provided a pre-taste of his work in Maastricht.

-
Bridging the gap between technology and clinical practice
Lee Bouwman, a vascular surgeon and endowed professor of Clinical Engineering, specialises in the implementation of groundbreaking healthcare technologies. The key to success, he says, lies in the collaboration between engineers and clinicians. This approach has already resulted in a range of...